AMM vs. Orderbook
An overview of capital efficiency within Interest-Rate Derivative and Cash-Flow Markets
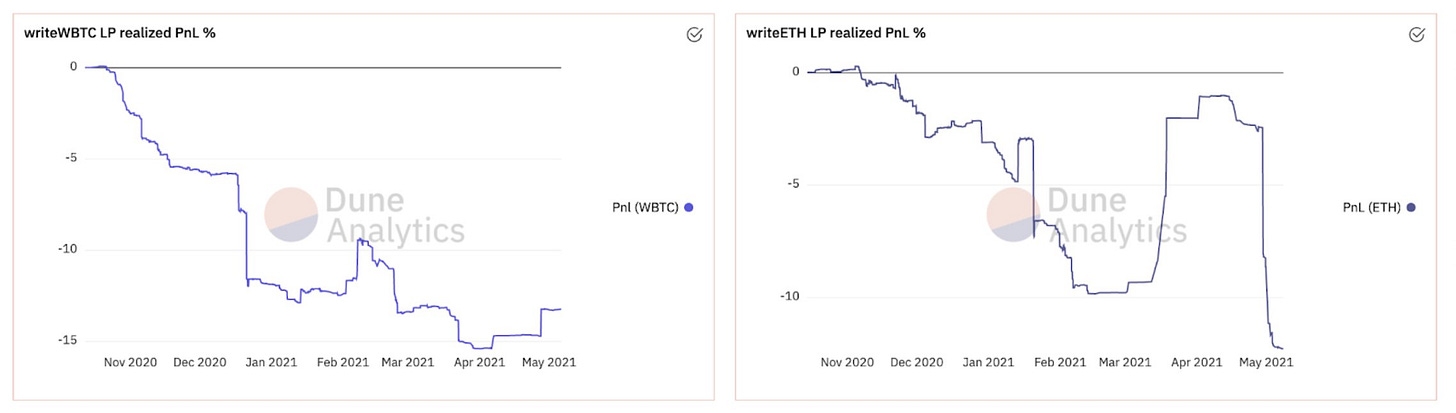
AMM's have insofar proven to be the effective mechanism for bootstrapping liquidity, however the efficacy and capital efficiency of AMM's within derivative markets has proven to be questionable at best.
Without the ability to adjust quoted prices with regard to standard derivative pricing variables, liquidity providers are exposed to significant risk and constantly give up an edge to the market. (As seen in LP returns)
Swivel instead attempts to bootstrap liquidity by providing the same token incentives present on most AMM's, but with the enhanced capital efficiency and flexibility that an orderbook can provide for all market participants.
In my previous article, “So… Why an Orderbook?” I walked through the reasoning behind our decision to implement an orderbook for interest-rates and cash-flow tokens.

As a quick TL;DR, the primary benefits are:
Increased general capital efficiency (similar to spot markets)
The ability for LPs to manage inventory with respect to:
Underlying rates
Time-decay (Theta)
Sensitivity to rate variance (Delta)
Underlying rate volatility (Vega)
Combined Principal Token and Yield Token liquidity pools (+100% capital efficiency)
Free limit orders + order cancellation
Instrument-Specific Optimizations
If then attempting to address Swivel's market with an AMM, one would need both a time-appreciating AMM for zero-coupon tokens (similar to Element), and a time-depreciating AMM for interest-coupons (similar to Pendle).
With Swivel's flexible orderbook, these separate AMM's are not necessary as a user can enter the marketplace with an underlying currency (USDC, ETC, BTC, etc.,), or alternatively with either zero-coupon tokens or money-market notional (interest-coupons) when exiting positions.
As a result Swivel's users benefit from the generalized efficiencies provided by an orderbook, and the further ~2x enhanced capital efficiency when compared to two separate AMM's.
Minting nTokens (Interest-Coupons)
Swivel’s issuance of interest-coupons, termed Notional Tokens (nTokens), is optimized in two ways:
nTokens include interest-generation and tracking functionality within their transfer function which:
Reduces the deposit overhead present in designs which require increasing deposits over time
Reduces complexity in nToken pricing
Allows interest to be redeemed at any time
Swivel atomically mints tokens as orders are filled which reduces the number of transactions necessary for most use cases.
Last updated